
Understanding your Brain
- The exproduct perience of pain, broadly speaking, is a of chemical messengers, emotions and thoughts involving pain.
- Pain messages travel along the spinal cord to the brain.
- Chronic pain reaches the hypothalamus which instructs the pituitary gland to release certain stress hormones.
- This is where our emotions are processed which explains why our feelings can influence pain.
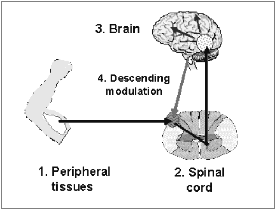
Central Sensitisation
- Some people are overly sensitive to stimulus (hyperpathia) while others may feel usually non-painful events as pain (allodynia).
Neuroplasticity
- Neuroplastic Changes : Pain can be caused by, or increased because of changes within the nervous system.
- structural and functional changes can occur at every level of the nervous system.
“Neuroplasticity can make it easier for you to feel tissue damage (acute) pain.”
- Neuroplastic changes related to pain can occur at multiple levels of the nervous system. More pain receptors may be in an area, the area of the brain that feels pain increases, the pain sensory system becomes more efficient, and the brain can learn pain.
Ability of the brain to change
- Neuroplasticity: refers to the ability of the nervous system to alter its structure and function.
- Neuroplasticity (also deals with brain plasticity, cortical plasticity and cortical re-mapping) refers to changes that occur in the organization of the brain and entire nervous system as a result of experiences. “Plasticity” relates to the learning by adding or removing connections, or cells.
